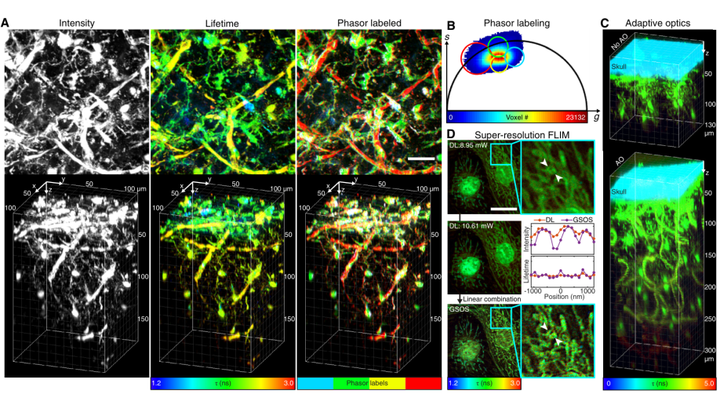
Abstract
Traditional fluorescence microscopy is blind to molecular microenvironment information that is present in a fluorescence lifetime, which can be measured by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). However, most existing FLIM techniques are slow to acquire and process lifetime images, difficult to implement, and expensive. Here we present instant FLIM, an analog signal processing method that allows real-time streaming of fluorescence intensity, lifetime, and phasor imaging data through simultaneous image acquisition and instantaneous data processing. Instant FLIM can be easily implemented by upgrading an existing two-photon microscope using cost-effective components and our open-source software. We further improve the functionality, penetration depth, and resolution of instant FLIM using phasor segmentation, adaptive optics, and super-resolution techniques. We demonstrate through-skull intravital 3D FLIM of mouse brains to depths of 300 µm and present the first in vivo 4D FLIM of microglial dynamics in intact and injured zebrafish and mouse brains for up to 12 h.
Publication
Optica, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 885-897

Assistant Professor of ECEE and BME
I am an Assistant Professor of Electrical, Computer & Energy Engineering (ECEE) and Biomedical Engineering (BME) at the University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder). My long-term research goal is to pioneer optical imaging technologies that surpass current limits in speed, accuracy, and accessibility, advancing translational research. With a foundation in electrical engineering, particularly in biomedical imaging and optics, my PhD work at the University of Notre Dame focused on advancing multiphoton fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and super-resolution microscopy, significantly reducing image generation time and cost. I developed an analog signal processing method that enables real-time streaming of fluorescence intensity and lifetime data, and created the first Poisson-Gaussian denoising dataset to benchmark image denoising algorithms for high-quality, real-time applications in biomedical research. As a postdoc at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), my research expanded to include pioneering photoacoustic imaging techniques, enabling noninvasive and rapid imaging of hemodynamics in humans. In the realm of quantum imaging, I developed innovative techniques utilizing spatial and polarization entangled photon pairs, overcoming challenges such as poor signal-to-noise ratios and low resolvable pixel counts. Additionally, I advanced ultrafast imaging methods for visualizing passive current flows in myelinated axons and electromagnetic pulses in dielectrics. My research is currently funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) K99/R00 Pathway to Independence Award.